Architecture Building Blocks (ABBs) in TOGAF
Introduction
Architecture Building Blocks (ABBs) are high-level, logical components that describe the essential capabilities and services an organization requires to meet its business objectives. ABBs are abstract and technology-neutral, focusing on what needs to be achieved rather than how it will be implemented.
Characteristics of ABBs:
- Technology-Independent: ABBs define the capability without specifying the implementation details (e.g., "Data Storage Capability" vs. "SQL Database").
- Reusability: ABBs can be reused across multiple projects, reducing duplication and promoting consistency.
- Alignment with Business Needs: ABBs are directly tied to business requirements, ensuring they support strategic goals.
- Modularity: ABBs are designed to fit together with other building blocks to form complete solutions.
Structure of an ABB
An ABB typically contains the following attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | A clear, concise name (e.g., "User Authentication"). |
| Purpose | A description of what the ABB does (e.g., "Provides secure access to applications"). |
| Capabilities | Key functions are provided by the ABB. |
| Relationships | Interactions with other ABBs (e.g., dependencies on Data Storage ABB). |
| Constraints | Business or regulatory constraints affecting the ABB. |
| Requirements | High-level requirements the ABB must fulfill. |
| Rationale | Justification for its inclusion in the architecture. |
Approach
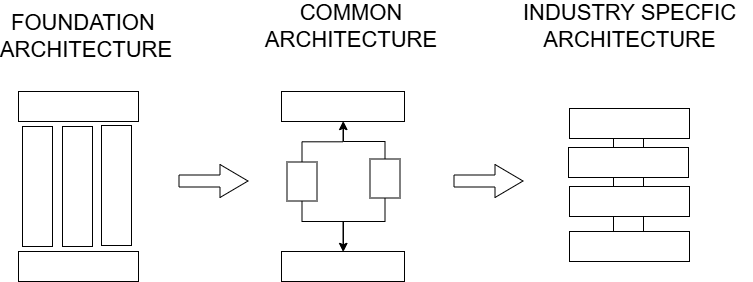
we can use left-to-right approach such as starting from foundation Architecture to Common System Architecture to Industry Specific Architecture.
Example : Starting with basic LMS system to Industry specific or College or University specific LMS and so on.
No Comments